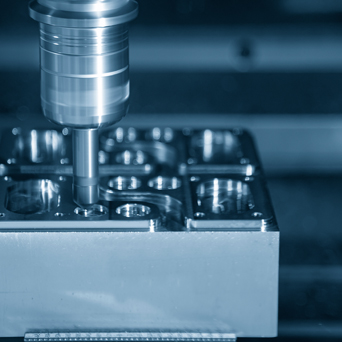
Do You Know the Safety Operating Procedures of Horizontal Boring Machine?
Horizontal boring machine is the most widely used type of boring machine. It is mainly used for hole machining, and the boring hole accuracy can reach IT7. In addition to enlarging the holes that have been cast or machined on the workpiece, the horizontal boring machine can also mill planes, drill, process end faces and flanges, and cut threads, etc. It is mainly used in single-piece small batch production and repair workshops, and the roundness error of machined holes does not exceed 5 micrometers, with a surface roughness of Ra0.63~1.25 micrometers. The main parameter of the horizontal boring machine is the diameter of the main spindle.
Composition of the Horizontal Boring Machine
A boring machine with a horizontally arranged spindle and a spindle box that can move vertically along the front column guide rail. When using a horizontal boring machine for machining, the cutting tool is mounted on the main spindle, boring bar, or flat rotary table. The required various speeds and feeds can be obtained through the spindle box, and it can also move up and down along the front column guide rail.
The workpiece is installed on the worktable, which can move longitudinally and horizontally with the lower and upper sliding saddles, and can also rotate around the circular guide rail of the upper sliding saddle to the required angle to adapt to various machining situations.
When the boring bar is long, the tailstock on the rear column can be used to support one end of it to increase its rigidity. In order to machine large holes away from the workpiece or long boxes, some horizontal boring machine increase the horizontal travel of the worktable by about twice, and increase the rigidity of the lower slide saddle by widening the main guide rail of the bed and adding an auxiliary guide rail.
Safety Rules for Horizontal Boring Machine
Follow the general safety operation regulations for milling and boring workers. Wear labor protection equipment according to regulations.
Check whether the operation handles, switches, knobs, fixture mechanisms, and hydraulic pistons are in the correct position, whether the operations are flexible, and whether the safety devices are complete and reliable.
Check whether there are obstacles within the effective operating range of each axis of the machine tool.
It is strictly forbidden to use the machine tool beyond its performance. Select reasonable cutting speed and feed rate according to the workpiece material.
When loading or unloading heavy workpieces, proper lifting equipment and lifting methods must be selected according to the weight and shape of the workpiece.
When the main spindle rotates or moves, it is strictly forbidden to touch the main spindle and the cutting tools installed at the end of the main spindle with hands.
When replacing the cutting tools, the machine must be stopped first, and the replacement can only be done after confirming. Pay attention to avoid damaging the blade.
Do not step on the guide rail surface and paint surface of the equipment or place objects on it. It is forbidden to knock on the workpiece on the worktable or straighten it.
After entering the machining program for a new workpiece, check the correctness of the program, simulate and run the program, and do not allow automatic cycling operation without trial to prevent machine failures.
When using the flat rotary radial tool holder for separate cutting, retract the boring bar to the zero position first, then switch to the flat rotary table mode under the MDA mode. If the U-axis needs to move, make sure that the U-axis manual clamping device has been loosened.
When rotating the worktable (B-axis) during work, make sure that it will not touch other parts of the machine tool or any object around the machine tool.
During the operation of the machine tool, it is forbidden to touch the rotating lead screw, rod, main spindle, and flat rotary table around the machine tool. The operator should not stay on the moving parts of the machine tool.
When the machine tool is running, the operator is not allowed to leave the work position without permission or have others watch over it.
When abnormal phenomena and noises occur during the operation of the machine tool, it should be stopped immediately, find out the cause, and deal with it in a timely manner.
When the spindle box and worktable of the machine tool are at or near the extreme position of motion, the operator is not allowed to enter the following areas:
Between the bottom surface of the spindle box and the bed;
Between the boring bar and the workpiece;
Between the boring bar when extended and the bed or worktable surface;
Between the worktable movement and the spindle box;
Between the rear bushing and the wall or oil tank during the rotation of the boring bar;
Between the worktable and the front main column;
Other areas that may cause squeezing.
When shutting down the machine tool, the worktable should be retracted to the middle position, the boring bar should be retracted, then exit the operating system, and finally cut off the power supply.
-

Classification of CNC Machine tools According to Control Mode
1. Open-loop control CNC centre latheThis kind of machine tool does not have the position detection feedback device and usually uses the stepping motor as the actuator. The input data is processed by ... -

Features and Capabilities of Horizontal Turning Lathes
When it comes to machining metal workpieces, horizontal turning lathes are essential tools in any workshop. These machines are designed to efficiently and accurately shape cylindrical workpieces by ro... -

A Detailed Introduction to CNC Lathe that Must Not Be Missed
CNC lathe is also called a computer numerical control machine tool, which is an automated machine tool equipped with a program control system. The control system can logically process the program with...